- Ah, the heat
- Guest Editor’s Column
- Art Moderne: Art Deco Furniture
- Lithograph Tin Toys
- Film Memorabilia
- Creative Impulse
- Hard Talk
- Possibility of Democracy in China
- In the News
- Artist Index and Statistics
- Market Insight
- Auction Reports : What happened
- Auction Reports : what's forthcoming
- Art Bengaluru
- Art’s Eye-view
- The month that was
- Photo Feature
- Roerich bridges Indo-Russian Cultural Relations
- Image and Symbol: Painters' Perceptions
- Image and Symbol: Sculptors' Perceptions
- My Window Shut to Open
- Paramjit Singh
- Mrinalini Mukherjee
- The Spirit of A Butterfly
- Have I Ever Opposed You?
- S(outh) E(ast) A(sia)
- Splitting the Other
- The Things That Happen When Falling in Love
- Millijunction
- Terminology
- Know your Act
- Different hues of Aakriti
ART news & views
Lithograph Tin Toys
Volume: 2 Issue No: 3 Month: 4 Year: 2010
Toy, basically a plaything for a child, has its own history of making from the very beginning of civilization in all diversified streams and cultures including our own country. We are to keep focus now on tin-toys which almost all of us are more or less acquainted with from our childhood. The most magnificent imagination provoking audible dynamic tin-toys supplied by the European as well as Asian manufacturing companies have become a classic and collector's item today. 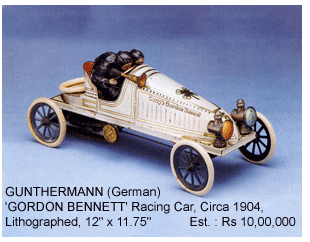 After 1960 & onwards when plastic & super alloy toys emerged in the market and in the backdrop of computerized games and toys these days, the subtle, sensible craft of tinplate toys which evolved from 1800 and through a long course of history reached an incredible height creatively blending technology and a parallel world of audio-visual imagination derived from reality and various folk cultures around gradually started to recede from our urban daily domestic schedules. Now early tinplate toys are becoming the most sought after collectibles throughout Europe and especially in the United States.
After 1960 & onwards when plastic & super alloy toys emerged in the market and in the backdrop of computerized games and toys these days, the subtle, sensible craft of tinplate toys which evolved from 1800 and through a long course of history reached an incredible height creatively blending technology and a parallel world of audio-visual imagination derived from reality and various folk cultures around gradually started to recede from our urban daily domestic schedules. Now early tinplate toys are becoming the most sought after collectibles throughout Europe and especially in the United States.
Tin-toys are made out of tinplate introduced in the 1800's initially to substitute wooden toys in Europe. The lithographed tin on which various colours and detail were printed on flat sheets of metal by a lithographic press used in making tin-toys, the tin plates were formed by dies and thereby assembled with small tabs. Colourful tinplate toys can more specifically be called tin-lithograph toys. In the printing industry through a special device of printing known as chromo-lithography tin-litho was worked out. A drawing was done on special stone with a grease pencil first. When wet the ink would adhere to the drawing and not to the wet stone. The drawing was then printed on paper, the process being similar to how a woodcut would work. A process of off-set lithography was introduced to print designs on tinplated sheets through the use of a rubber roller in the late 1800's. By the 1930's the process was further perfected and the machines became capable of printing designs on 50 tinplates per minute and it proved to be the real turning point for the tin-toy manufacturers.
The early decades of the 20th century saw Germany lead the manufacturing of tin-toys and this German domination continued till the outbreak of the 2nd world war. Earnst Paul Lehmann, the renowned German manufacturer of tin-toys is said to have exported 90% of his toys. 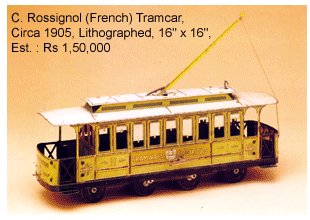 To keep pace with the growing attractive tinplate toys many new companies came up in France and England like Rossignol factory and Chad. When British people shunned most of the German products, Chad kept on marketing their products under the name of Chad Valley Toys.
To keep pace with the growing attractive tinplate toys many new companies came up in France and England like Rossignol factory and Chad. When British people shunned most of the German products, Chad kept on marketing their products under the name of Chad Valley Toys.
In Japan tinplate toys first appeared in Meiji and Taisho era and Japan's own tradition of making tin-toys continued as long as the Europeans although it started to peak from 1940 onwards and thereby highly developed in 1950's and 60's. Around 1874–75 imported tin plate was used in oil cans which they collected as raw materials while the inspiration mostly came from the German tin-toys available in Japan. As Japan managed to arrange their own printing technology and derived technology of clock work from Germany, it gradually became the reputable tin-toy producing centre leaving behind Germany in the aftermath of 1st world war. Japan continued to produce very high quality of tin -toys even after 2nd world war. Under the American occupation in Japan, Japanese tin-toy industry was granted a right to resume its operation and export in 1947. It undoubtedly helped Japan to reach its height in the business. Apart from wind-up and friction driven toys Japanese tin-toys were probably the first to be powered by batteries and able to provide flashing lights and sounds. The range of companies in the Japanese tin-toy industry was enormous.
China began to produce tin-toys in the early 1920's, but their products were primitive and poorly made. 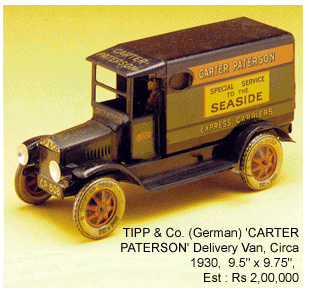 After the decline of overpowering Japanese tin-toy industry China assumed the leading role in the world of tin-toy industry. Chinese products are manufactured in a comprehensibly higher scale of perfection and at the same time they are being marketed in affordable prices. The cultural revolution of China played a vital role to boost the industry in the 1970's.
After the decline of overpowering Japanese tin-toy industry China assumed the leading role in the world of tin-toy industry. Chinese products are manufactured in a comprehensibly higher scale of perfection and at the same time they are being marketed in affordable prices. The cultural revolution of China played a vital role to boost the industry in the 1970's.
USA has a long history of tin-toy making. Since 1850 when there were at least 50 tin-toy makers operating in and around Connecticut and simultaneously Philadelphia was also a noted manufacturing centre. Brooklyn's Buckman Manufacturing Co. first produced a steam-powered tin-toy around 1872. The United Stated is supposed to be the place where mass production of tin-toys sprung out and thereby floodgates were opened for an industry which thrived well in to late 1950's. Some of the most desirable tin-toys were produced by Walt Disney during that period of time.
Paya Company (1902), the local tinsmith of Spain initiated the production of tin-toys which were considered equal in standard with the tin-toys of the North. Paya just recently shut down its operation.
During the late 1960s, many Indian companies also manufactured tin toys but they did not match the international parameters.
There is a wide and exciting range of tin-toy items. It includes robots, tin animals, tin-car & motorcycles, air, sea & rail items and insects.